Introduction¶
The payment-gateway module offers a flexible payments model which allows multiple payment gateways to co-exist in a single Tryton database. The logic for storing payment profile and transactions are decoupled from the gateway specific implementation itself making it easy to create custom payment gateways with their own processing logic and feature sets.
Payment Gateway¶
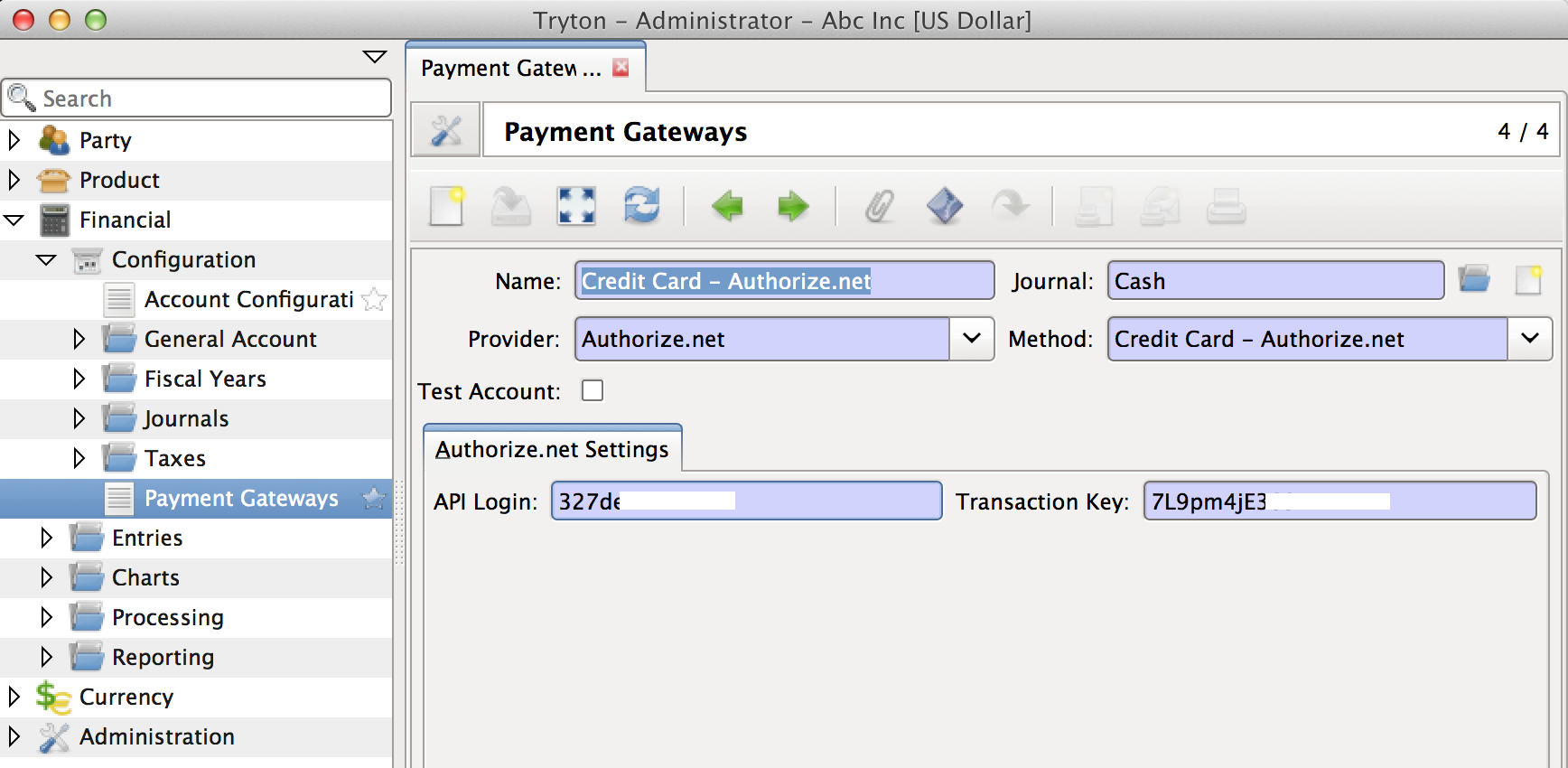
Payment gateway represents a specific method of payment by a specific provider (like Authorize.net, Paypal etc.). Each payment gateway may require additional configuration settings specific to it.
Payment Profile - Store Credit Card data¶
Several payment gateway service providers offer a secure way to store confidential customer credit card information on their server. Transactions can then be processed against these profiles without the need to recollect payment information from the customer, and without the need to store confidential credit card information in Tryton.
This model represents a profile thus stored with any of the third party providers. The module only stores the last 4 digits and expiration date in the database. Remaining confidential information is stored on the payment service providers server and a reference to the same is stored in the provider_reference field.
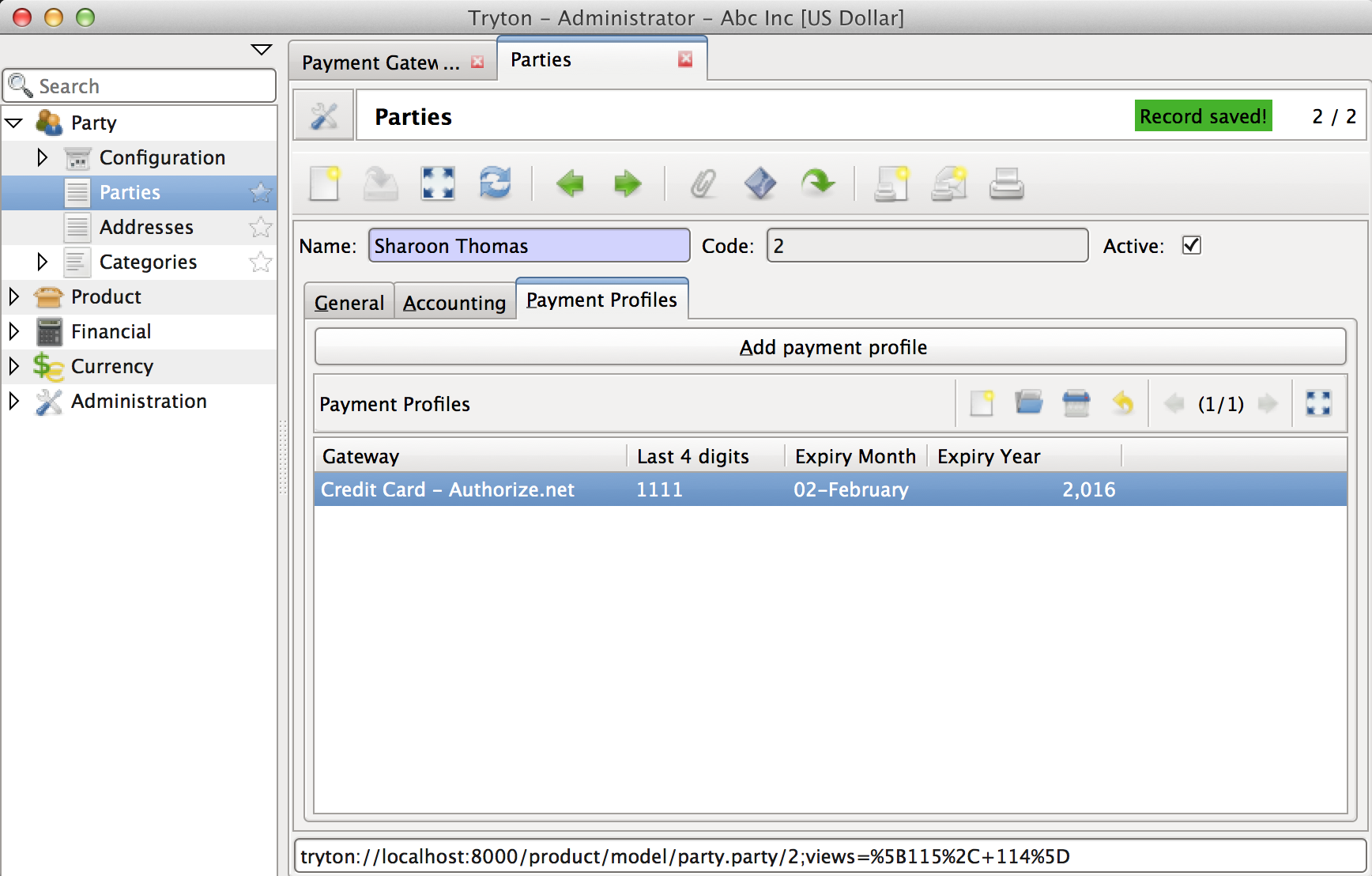
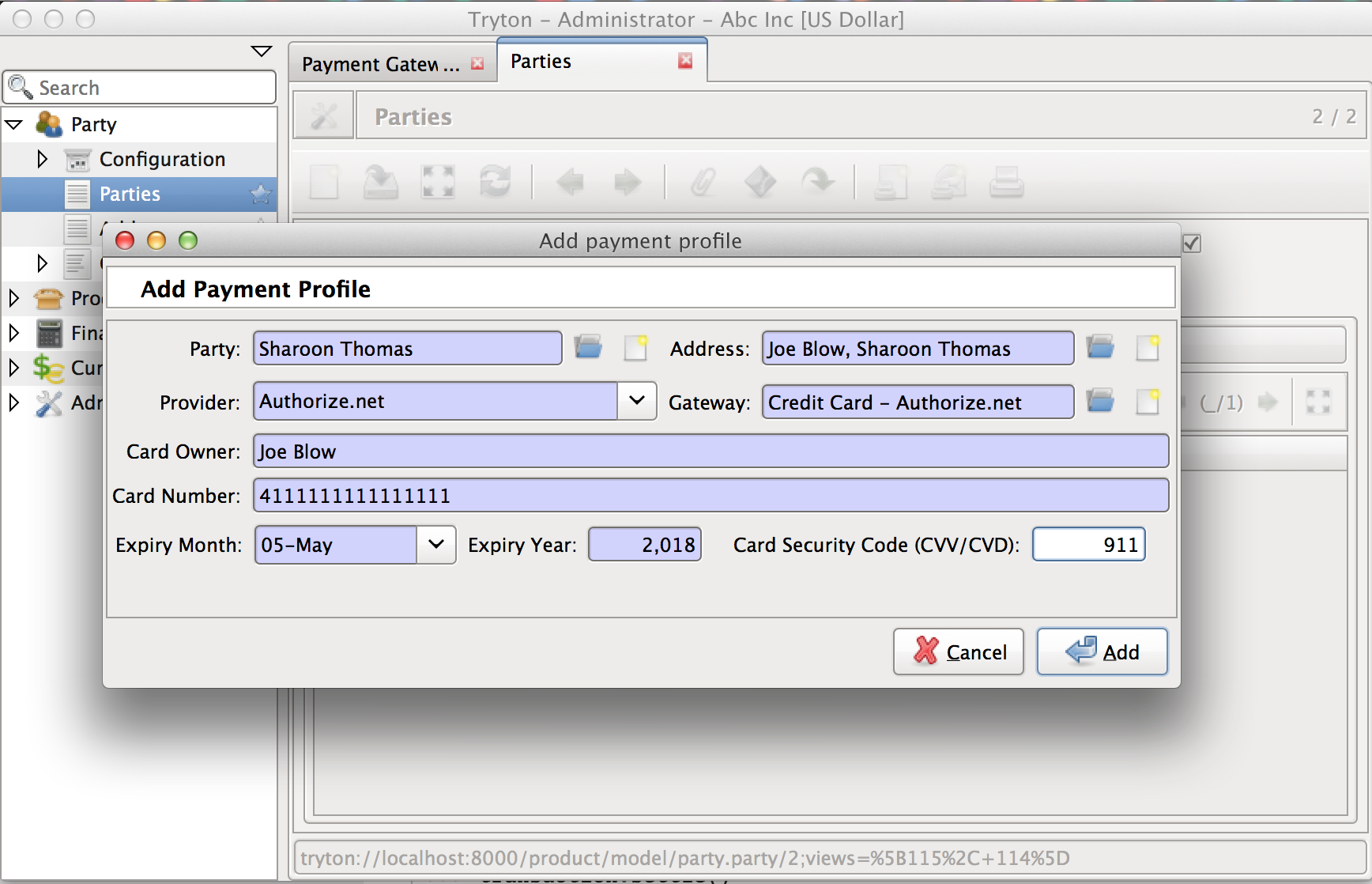
See PaymentProfile.
Payment Transaction¶
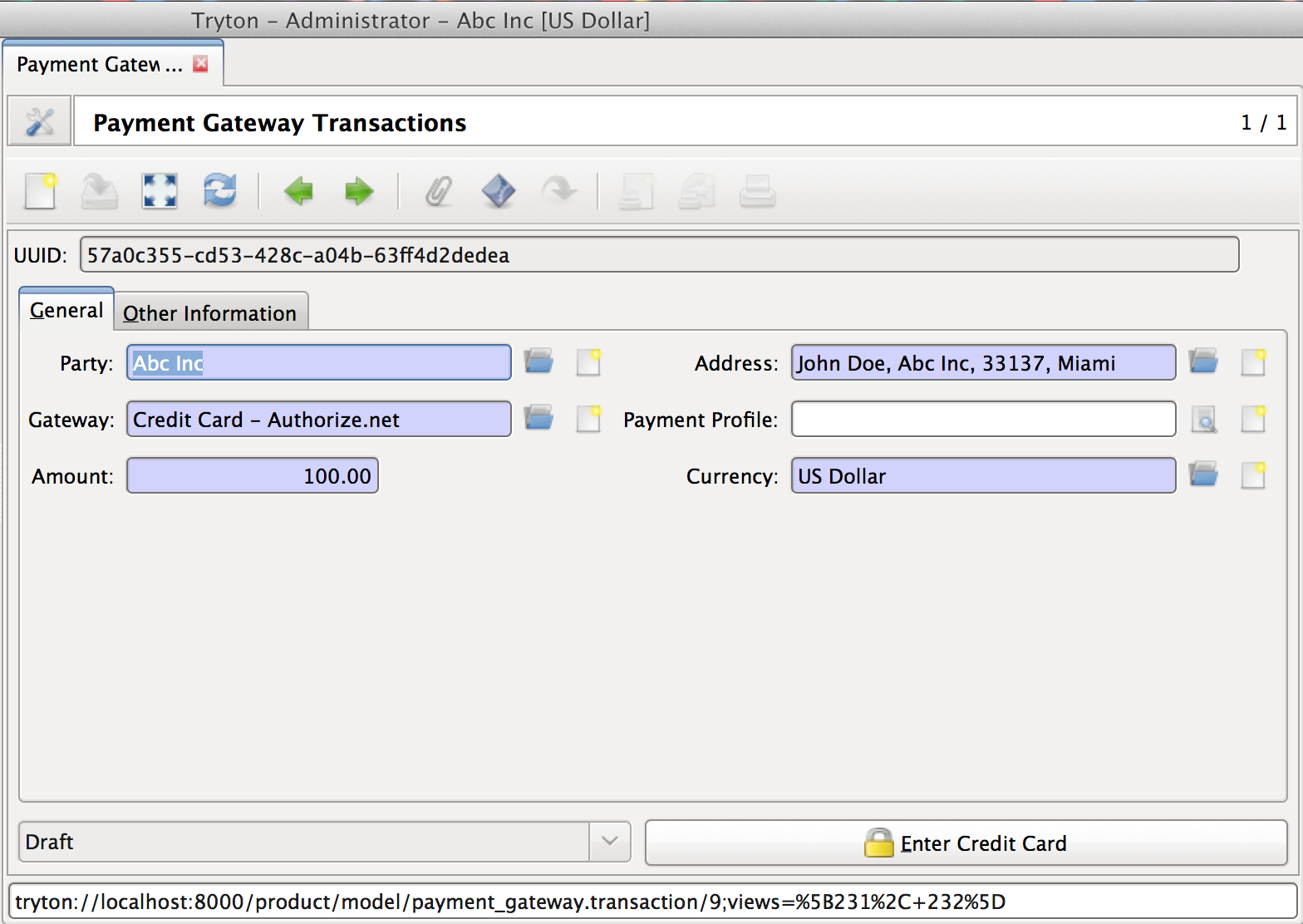
The transaction model stores and tracks payments that are made using the payment gateways.
When a transaction is created, it is assigned a unique uuid.uuid4(). This is used as transaction reference when transactions are sent to payment gateways. Without this identifier, some providers mistakenly report duplicate payments.
See PaymentTransaction.
States of a Transaction¶
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| Draft | The transaction is just being filled by the user. This is the default state where every transaction begins |
| In Progress | Some gateways do not immediately return a success of failure of a transaction. Such transactions could be moved to the in-progress state and the status of the transaction is queried later to see if the transaction succeeded or failed. |
| Failed | The transaction failed. The reasons can be seen from the logs. |
| Authorized | The transaction has been authorized, but not settled. |
| Completed | The transaction has been captured, but the account moves itself, has not been created within Tryton. |
| Posted | The transaction is complete and the necessary account moves have also been created. |
| Canceled | The transaction was cancelled. |
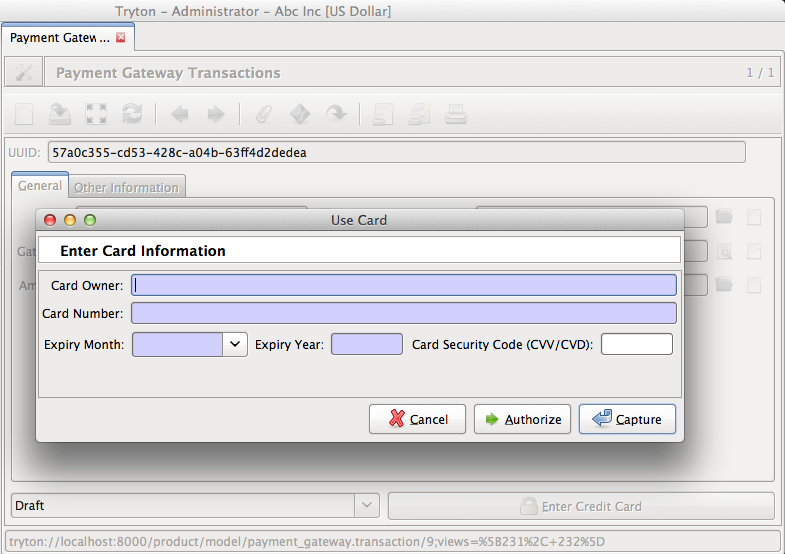
Transaction using payment profile¶
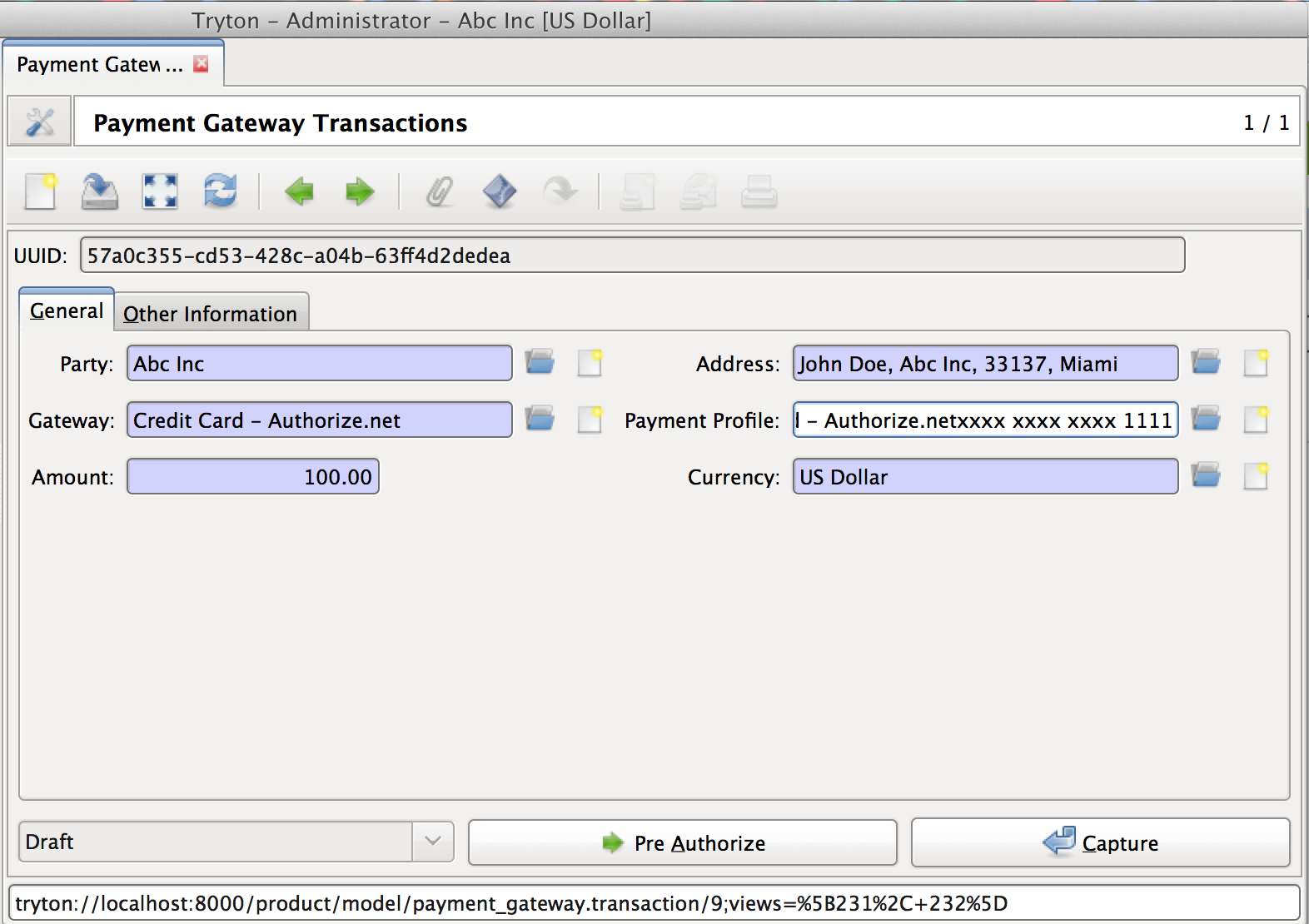
Safe Posting¶
Completion of a successful payment gateway transaction also includes creating the corresponding accounting entries in Tryton. But, creation of account move requires a journal with proper debit and credit accounts (not required when the journal is created) and a fiscal period to exist on the date of the transaction. Hence, if the system was to make the account move along with the transaction capture or authorization, it could lead to inconsistencies since the capture/authorize could have already been completed on the payment gateway but the creation of account move might result in the failure of the entire transaction change.
To solve the problem, the design introduces a completed stage during which no account moves are created. This state makes a transition with minimal scope for error (a single state field is update), to be available. This is important since a transaction rollback due to any error could lead to Tryton having an inconsistent state of the transaction compared to the gateway.
In addition to this the transaction model offers a safe_post() method which tries to post the transaction, but leaves the transaction in the current state on failure. The user could later look into the completed transaction and post them manually.
Payment Transaction Log¶
The transaction log model stores responses from the payment service provider. When a response is is received from a payment service provider, it could be passed onto TransactionLog.serialize_and_create(), which would then serialize the response object as YAML and store it. The responses can be useful in identifying the reason why a transaction may have failed.